Evolution of US autogas consumption and refueling infrastructure
Propane is a reliable alternative fuel used to power various vehicles, including medium-duty delivery vans and heavy-duty buses and trucks. It can produce lower greenhouse gas emissions and pollutants and is cheaper than gasoline and diesel. However, some propane-fueled vehicles, particularly school buses, have faced tough competition from electric vehicles and from a regulatory environment favoring other alternative vehicle fuels in recent years. Here, we explore U.S. autogas consumption trends from 2018 to 2022, along with changes in autogas vehicles and station counts. Demand data is sourced from the Propane Education & Research Council (PERC), while the vehicle and station data come from the Alternative Fuels Data Center (AFDC).
Commentary
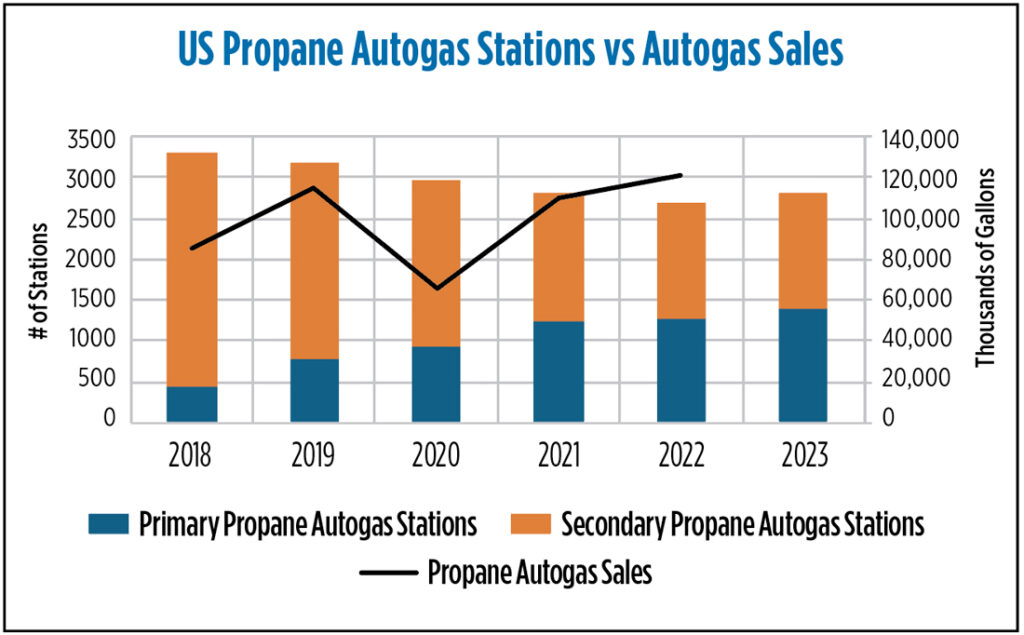
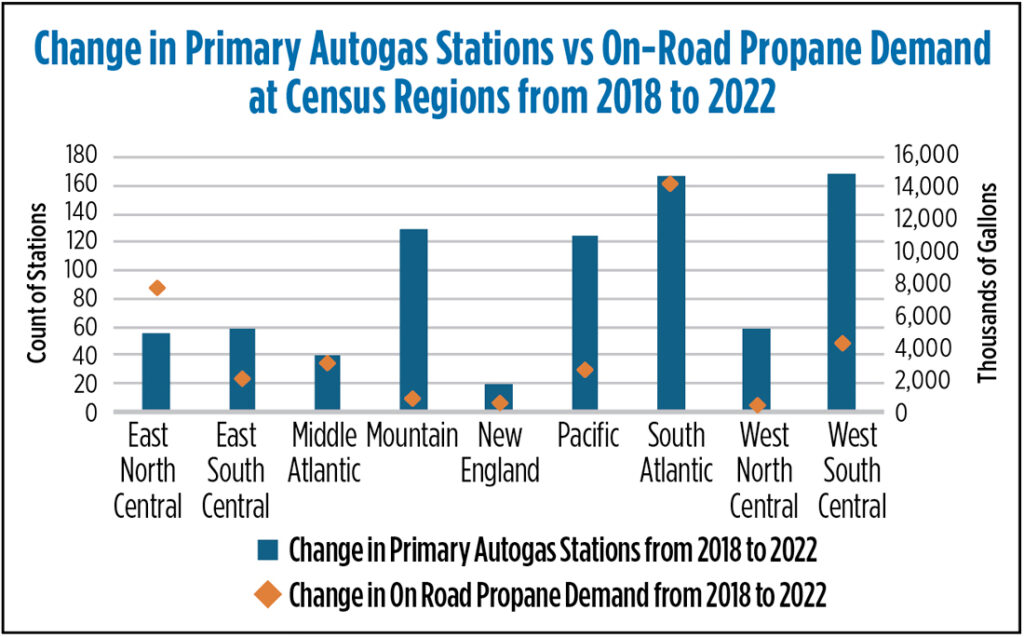
⦁ Autogas sector demand: Since 2018, propane consumption in the autogas sector has been on the rise. The sector used about 85.6 million gallons in 2018, increasing to 114.8 million gallons in 2019. The 2020 pandemic caused a dip in demand due to lockdowns and travel restrictions, but by 2021, it rebounded to 110.0 million gallons as economic activities resumed. Post-2021, ICF estimates show an average demand of 127.1 million gallons for 2022-23. Key factors influencing demand include fuel prices, environmental regulations and the rise of alternative fuels like electric vehicles. From 2018 to 2022, the South-Atlantic region, particularly Florida, saw the highest increase in autogas demand.
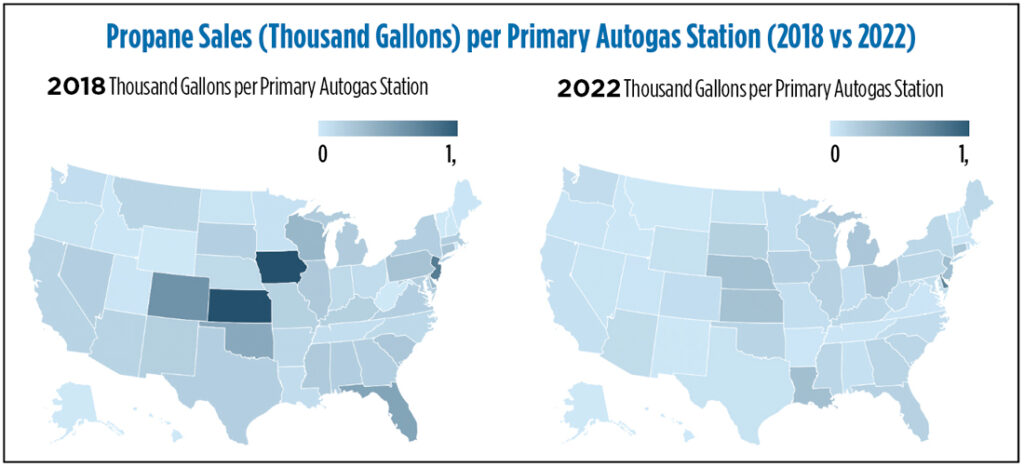
⦁ Propane autogas stations: The total number of propane autogas stations in the U.S. has been declining, but primary stations capable of vehicle-specific fueling have been increasing since 2018. Secondary propane stations, which offer limited vehicle fueling services, have been declining, with some speculated to have converted into primary stations. As primary stations grow, the vehicle density per station has decreased. In 2018, each primary autogas station supplied an average of 190,200 gallons of propane for on-road vehicles, dropping to 95,700 gallons by 2022. The West South-Central region saw the most significant change in primary autogas stations from 2018 to 2022. Texas saw a fivefold increase in primary stations, while California’s number more than doubled. In 2023, Texas, California, Florida, Michigan and Ohio had the highest number of primary and total stations, with Florida leading in autogas consumption, supplying approximately 178,200 gallons per primary station.
⦁ Propane vehicles: Between 2018 and 2022, propane vehicles grew at a compound annual growth rate of 7 percent, according to the Clean Cities and Communities Alternative Fuel Vehicle Inventory. However, their market share in the U.S. vehicle market fell from 2.7 percent to 2.2 percent due to rising competition from electric vehicles and battery technologies, as well as a limited refueling station network.